Here's the video link for those who don't like to read:
Introduction:
The architecture of an electric vehicle (EV) two-wheeler
system can vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer. However, here’s
a general overview of the key components and their interactions in an EV
two-wheeler system:
§ Battery Pack
§ Electric Motor
§ Motor Controller
§ Vehicle Control Unit (VCU)
§ Battery Management System (BMS)
§ Power Electronics
§ User Controls
§ Instrument Cluster
§ Regenerative Braking System
§ Communication Interfaces
The design and development stages for manufacturing an
electric vehicle (EV) two-wheeler involve several steps that encompass concept
development, engineering, prototyping, testing, and production planning. Here's
a detailed overview of the typical stages involved:
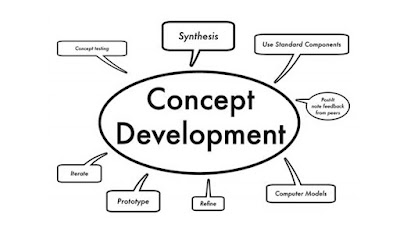
Concept Development:
Identify the target market, customer needs, and market
trends.
Conduct market research and gather insights to determine the
product's features, performance, and price range.
Develop a design concept, considering factors such as
aesthetics, functionality, and market positioning.
Design and Engineering:
Create detailed design specifications based on the concept,
incorporating considerations like aerodynamics, weight distribution, and
structural integrity.
Design the chassis, body, suspension, drivetrain, and other
key components.
Use computer-aided design (CAD) software to generate 3D
models and perform virtual simulations and analysis, including structural,
thermal, and fluid dynamics.
Optimize the design to meet performance, safety, and
regulatory requirements.
Battery and Powertrain Development:
Design and integrate the battery pack, motor, motor
controller, and power electronics into the vehicle.
Perform system-level simulations and analysis to optimize
powertrain efficiency and thermal management.
Prototype Development:
Source and integrate components from various suppliers.
Conduct extensive testing and validation, including
performance testing, durability testing, and safety testing.
Refine the design and make necessary adjustments based on
the results of prototype testing.
Regulatory Compliance:
Perform necessary tests and obtain certifications from
regulatory bodies.
Address any design modifications or improvements required
for compliance.
Manufacturing Process Planning:
Identify manufacturing equipment and machinery requirements.
Define production line layout and workflow, considering
efficiency, ergonomics, and safety.
Supply Chain Management:
Ensure the availability and quality of components to meet
production demand.
Implement inventory management systems to optimize supply
chain efficiency.
Tooling and Production:
Set up the production line and initiate small-scale
production runs.
Implement quality control processes and inspection
procedures at each production stage.
Monitor and refine the manufacturing processes to improve
efficiency and quality.
Post-Production Testing and Validation:
Perform functional testing, durability testing, and
environmental testing.
Address any issues or defects identified during testing and
make necessary improvements.
Launch and Market Entry:
Establish sales and service networks.
Monitor customer feedback and make continuous improvements
based on user experience.
Conclusion:
It's important to note that the design and development stages may overlap, and iterations and refinements are common throughout the process. Additionally, regulatory compliance requirements may vary depending on the target market and specific regulations governing electric vehicles.